

3D Printing: Which Filament Should I Choose?
Whether you are considering buying your first 3D printer or are an experienced user, an overview of filaments (printing materials) can be useful for all. We will look at the basic types of filament, their key properties, and highlight any risks associated with their use.

3D Printing: How to Choose Filament - CONTENTS
- What are Filaments?
- Filaments - Properties and Parameters
- Other Properties to Watch Out For
- Filament Overview: Which 3D Printing Material Should I Choose?
What are Filaments?
Filaments are the string-like fibre used in 3D printing that bring your models to life. Filaments are sold on reels. Many types of filament are made from pure plastic but there are also plastic filaments with additives, and even those made from completely different materials. The following article should give you the help you need to choose the optimum filament for your latest project.
Filaments - Properties and Parameters
When choosing a filament, it is vital to look for certain properties and parameters that should correspond not only to the capabilities of your printer but also with what you are planning to print. Get this right and you will avoid compatibility issues, printing complications and deformations in your final model. Every home printer should provide the following parameters, which you can set in product filtering at Alza.cz.
- Diameter: filaments are sold with several diameter values. The most common are 1.75mm and 2.85mm (also referred to as 3mm). Always make sure which diameter your printer requires before buying filament.
- Material: different materials have different characteristics that are essential for print quality. We will focus on specific materials later in this article.
- Maximum nozzle temperature: 3D printing materials melt at different temperatures and the nozzle temperature corresponds not only to the requirements of the particular material but also to printing speed. Slower (higher quality) printing requires a lower nozzle temperature (for slower melting), while faster printing requires faster melting—hence it needs a higher nozzle temperature. The "maximum nozzle temperature" indicates the maximum value in °C.
- Bed temperature: A heated bed is a prerequisite for optimal 3D printing, although it is not a feature on all printers. The bed needs to maintain a specific temperature to hold material together and to prevent deformations that can be caused by unwanted cooling.
- Flexibility: Flexible filaments produce elastic results. Models made with low flexibility may rupture under stress, while highly flexible filaments will stretch and bend.
- Temperature Resistance: This parameter specifies the range of temperatures a material can withstand after it is printed.
Other Properties to Watch Out For
Filaments also have other properties, which can be difficult to express with fixed values. Nevertheless, their presence may be essential with regards to the final use of products. Here is a list of the most important.

- Odour: some materials may give off an unpleasant smell during printing.
- Toxicity: Printing fumes sometimes have a detrimental effect on human health; in some cases, nausea may occur.
- Biodegradability: some filaments are biodegradable and/or compostable, while others may cause damage to the environment.
- Recyclability: Another way to print environmentally is to use recyclable materials or those that have already been recycled.
- Contact with food: not all materials should be left in contact with food, some may contaminate food with toxic substances, others with unwanted bacteria.
- Heated bed: Certain materials require that the 3D printer's bed be heated to ensure your models hold correctly, there is no uncontrolled expansion, contraction or other deformation.
Filament Overview: Which 3D Printing Material Should I Choose?
We have briefly explained the basics of printing filaments. Now it's time to talk about the most popular materials. When you have decided what you want to print, you need to choose the appropriate filament. Some materials are incredibly versatile, while others are suitable for only a limited number of applications.

PLA
If you are looking for a filament that is versatile and popular in the 3D printing community, PLA is the answer. Polylactide or polylactic acid is a type of plastic that is not made from oil but from vegetable carbohydrate sources (e.g. cornstarch), so it is bioplastic. As a result, PLA is biodegradable, produces no odour or toxic fumes during printing, and is considered safe to come into contact with food. However, this feature may not be guaranteed for all specific filaments, so do check what the manufacturer says.

PLA is a user-friendly material and it is relatively easy to work with. It melts easily (at approx. 180°C) and does not necessarily require a heated bed as it does not expand or contract significantly during printing. Although PLA is a versatile material that fits most applications, it is not very flexible and can be fragile. It is not suitable for use in places where bending or similar deformations could occur. It is also necessary to bear in mind the low-temperature resistance—deformation can occur on products at 60°C.
PETG
Another popular filament is PETG, a glycol-enriched variant of classic PET that everyone knows, for example, from plastic bottles. It is a material that is relatively easy to print. However, unlike PLA, it is durable, strong, and somewhat flexible. It can withstand applications where it is subject to bending, twisting, or severe impacts (PETG makes great phone cases). The recommended print temperature starts at 220°C.
PETG is resistant to temperatures up to 80°C and requires a heated bed. In terms of contact with food, the situation is similar to PLA - it is best to check the information from the manufacturer of a particular filament. We always store PETG filaments in a dry place as they easily absorb air humidity.
ABS
ABS is a material known for its physical and temperature resistance. Models made with ABS can withstand temperatures up to 100°C, considerable stress and strong impacts. The price for this durability is a more demanding printing process. The temperature of the printed material must be at least 210°C and a heated bed is necessary (at least 80°C) as ABS tends to deform with uncontrolled cooling. It should definitely not be used in products that will come into contact with food. ABS is made from oil and is NOT biodegradable.

TPE
TPE filaments are what you need when printing flexible and elastic products. They are very durable and flexible—they resist bending, torsion and other deformation more than any other printing material. Printing from TPE filaments is normally more demanding, but does not require a heated bed. These materials are not considered suitable for contact with food, on the other hand, they are recyclable and should be biodegradable.
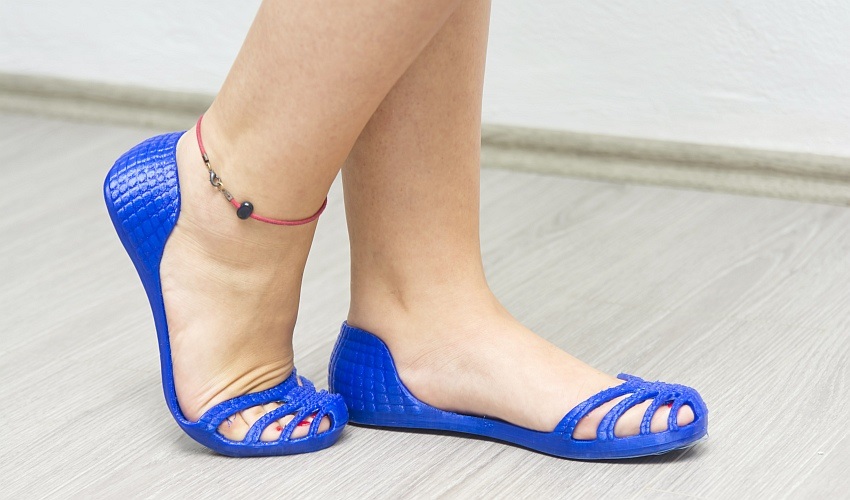

TPE is often used as a filament for printing shoes but it is also suitable for other applications where its properties come in handy, such as seals. TPE32 and TPE88 indicate flexibility. While a lower number (TPE32) indicates a harder material, TPE88 is a softer material.
Nylon
High strength, durability, thinness and flexibility are the characteristics that define nylon as a filament for 3D printing. It can withstand all kinds of stresses, but printing is not straightforward and the optimum extruder temperature is around 250°C. Printing nylon requires a heated bed. Nylon can absorb a variety of dyes, both before and after printing. One disadvantage is that it absorbs humid air. This means it should always be stored in a dry place.
PC (Polycarbonate)
Like nylon, PC (polycarbonate) is a very strong material. It is one of the strongest commercially available filaments. Its is highly-resistant to shattering, breaking and other forms of damage. It is also resistant to heating above 100°C. Printing takes place at very high temperatures (sometimes even more than 300°C) and it needs a heated bed (around 100 ° C).
One of the key characteristics of polycarbonate is its transparency and, as it is so strong, it is ideal for extreme applications such as bulletproof glass. PC models can be used in the home environment for heavily stressed mechanical components and various protective cases. Polycarbonate is biodegradable and easily recyclable but contact with food is not recommended.
There are a plethora of filaments for 3D printing. We have only given you a very basic overview of the ones most commonly used. Before buying filament, think about the properties you require to make your final model a success.





