What Is HDR and How Does It Work
HDR is an abbreviation that you often see nowadays when selecting a television. What exactly does it mean? How does HDR work in practice? And is it worth investing in a HDR television? These and other questions will be answered in this article.

High Dynamic Range, HDR in short, is a video standard that enhances the brightness and contrast.
What does this standard look like in practice? Imagine shooting a scene of a beach with the setting sun. Without HDR processing, the darkest and brightest parts of the scene dominate the image, but otherwise no other shades have any definition.
But if you shoot the same scene in HDR, you will see all the details. In short, the image will be closer to what you actually see when watching the view.
How HDR Photography Works
HDR image processing technology has been used for photos for several years and is associated with so-called bracketing. This is the process whereby the camera takes two shots when the shutter-release button is pressed (more powerful cameras can shoot even more): one shot records all the dark details while the other records bright details and the camera blends the shots to create the final image.
 Bracketing eliminates overexposed (highlights) and underexposed (dark to black) locations. In general, in an image dominated by a bright sky, the rest of the scene is very dark, and similarly, interior shots show a white spot where a window should be.
Bracketing eliminates overexposed (highlights) and underexposed (dark to black) locations. In general, in an image dominated by a bright sky, the rest of the scene is very dark, and similarly, interior shots show a white spot where a window should be.
In HDR shooting, however, it works differently: images are created with a single exposure value, but with a much larger dynamic range. In the image, the dark and bright portions are well defined.
What is the Dynamic Range of a Scene
Now that we know how HDR works, we can define the dynamic range: it is the difference between the above-mentioned brightest and darkest points. The greater the difference, the greater the demands on the dynamic range of the camera or the camera's sensor.

An illustrative example of a case where the camera's dynamic range is considerably smaller than the scene's range can be seen in the figure above on the left. Next to it is a shot taken with a camera with a sufficiently high dynamic range. With cameras, it works similarly to shooting a video.
Benefits of HDR in Televisions
We've explained how HDR is created and the principle of dynamic range, and finally, we can describe the benefit of dynamic range in televisions.
The dynamic range of a television means the difference between the darkest and lightest points that the TV panel can display.
If this information seems unimpressive so far, don't worry, because there's more to it: HDR televisions are capable of achieving brightness from 0.00005 cd/m2 to over 1000 cd/m2. Thus, bright spots appear brighter and darker shades look darker without loss of detail and with high fidelity in colour rendering.
The result is a more realistic and colourful, faithfully reproduced image with sharper details in dark and bright places. The image on the TV will be a faithful reproduction of what your eyes would see if you were present during the shoot.
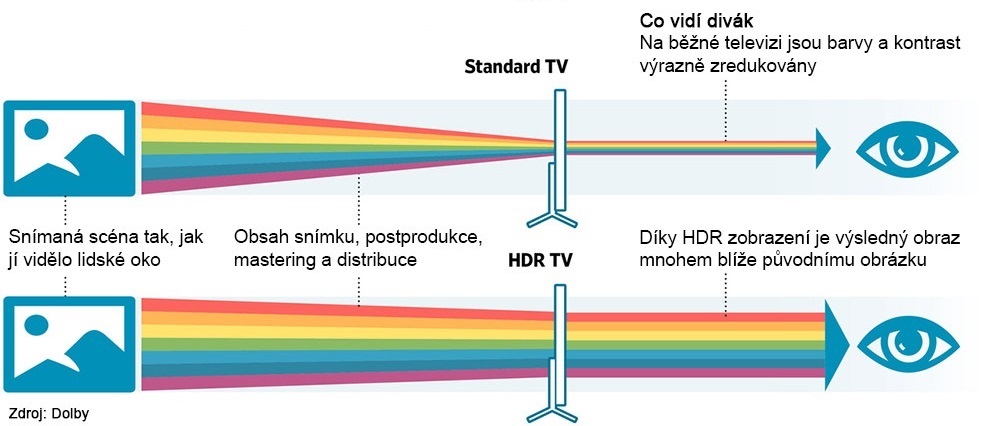
HDR Displays Many More Colours
HDR video also differs from the standard colour gamut. It describes what part of the colour model the TV is capable of displaying, or how many shades of colours the panel can reproduce.
Because HDR televisions allow for much better colour reproduction, Rec.2020 (BT.2020) has been introduced. If the HDR TV receives content standardised using Rec.2020, it is able to display a larger quantity of colours than TV's without HDR technology.
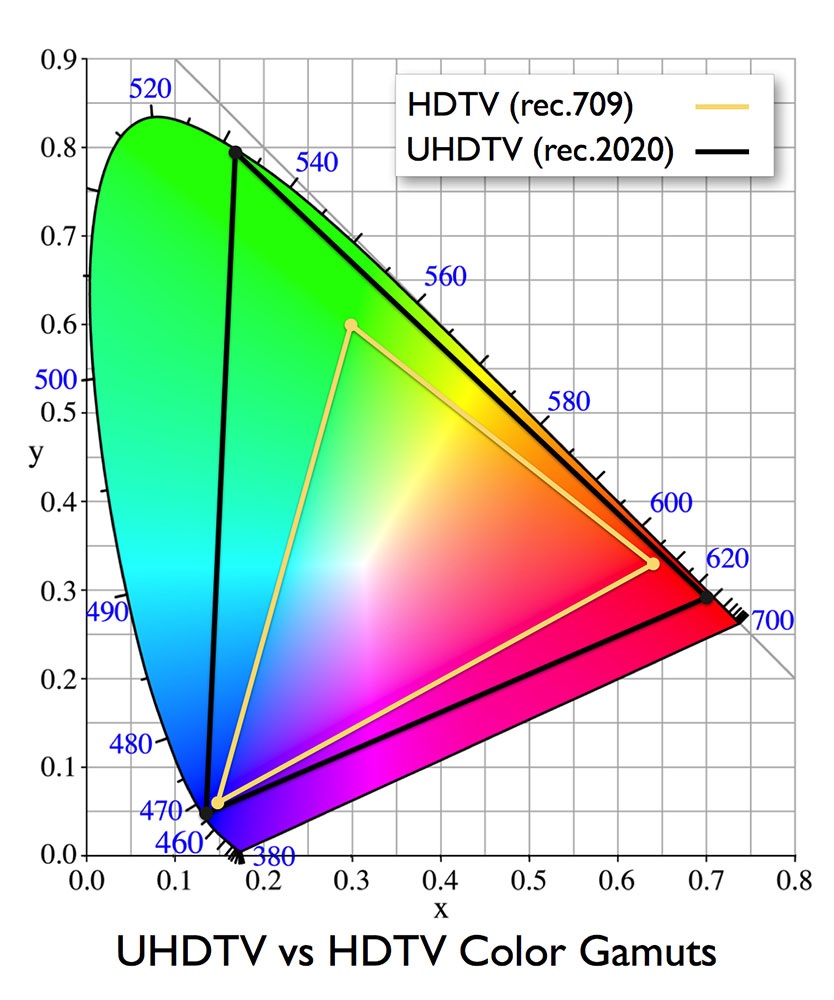
HDR Televisions have a Greater Colour Depth
The drastic difference between non-HDR and HDR TVs is also evident in the colour depth values. This indicates how many bits are used to describe a particular colour or pixel.
The higher the colour depth, the more detailed the colour scaling and the finer the gradients between the shades. HDR video standards are based on 10-bit and even 12-bit colour depths, while Rec.709 TVs use an 8-bit depth.
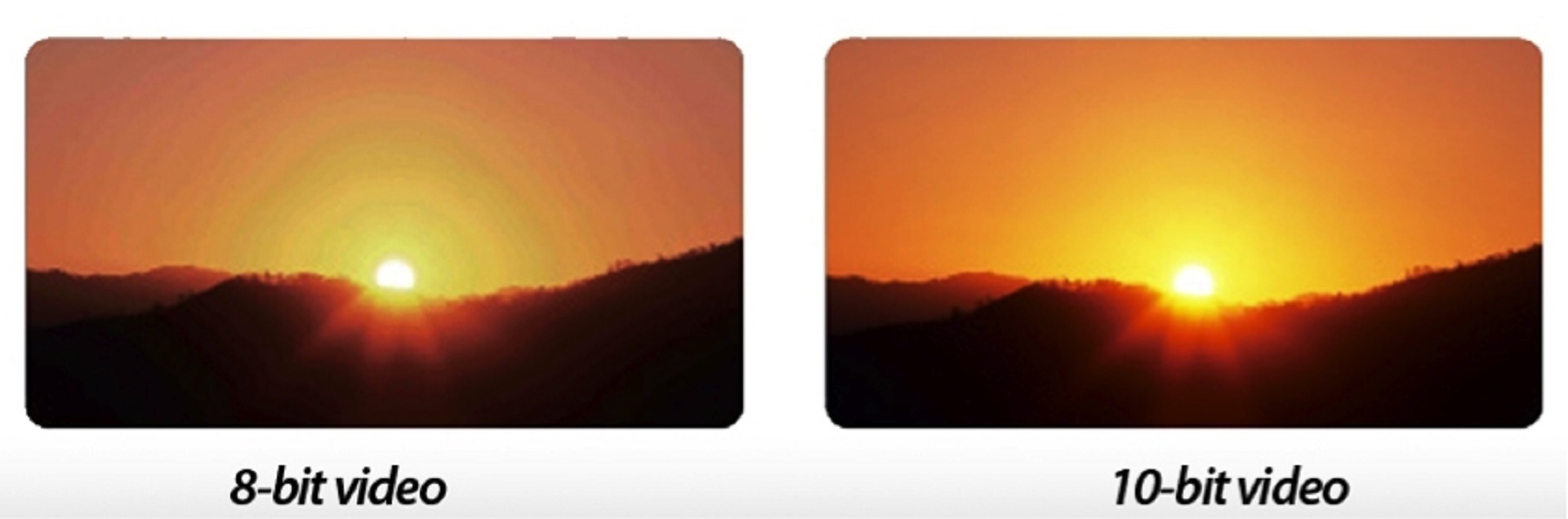

Now hold on: 8-bit depth allows you to display 16 million colours, while 10-bit can handle over a billion. With 12-bit processing, you get almost 69 billion colours!
I want to view images in HDR. What do I have to do to achieve this?
As you might be able to guess by now, just buying an HDR TV that supports a wide range of realistic colour shades is not enough. To maximize the potential of this state-of-the-art technology, the entire circuit must be designed to support HDR.
The basic requirement is an HDR television that can play at least one of the four HDR formats. Specifically, the formats are HDR10, Dolby Vision, HLG and Advanced HDR.
Out of the television models released in 2017, LG is the only manufacturer to support all four formats. On the other hand, Samsung, which has been inclined from the beginning to the HDR10 format, remains exclusively with this format, along with as Philips. Sony and Hisense have announced support for both HDR10 and Dolby Vision formats.
The HDR10 format enjoys wide support, mainly because manufacturers do not have to pay to use the standard. Nearly all the higher ranges of this year's HDR televisions support the format. In terms of supported technologies, however, Dolby Vision is probably the most advanced, so it is expected to be used in cinemas.
If you want to watch HDR broadcasts, the signal broadcast to your TV must support one of the four HDR formats. If you prefer to watch movies from discs, you will need to buy HDR 4K Blu-ray discs (mostly available in HDR10 format, but some Dolby Vision BR discs are available).
However, videos with a high dynamic range are available on YouTube (HLG codec), Netflix, Amazon Prime (both companies use HDR10 and Dolby Vision) or VuDu.

As for gaming consoles, HDR supports Xbox One S, PlayStation 4 Pro and NVIDIA Shield. However, you need to connect to your TV using an HDMI 2.0 cable or higher. This is the only way to support Rec.2020 and HDR.
Does all of this seem too complicated? Fortunately, you can get help by looking for the Ultra HD Premium brand:

Ultra HD Premium is a certification that aims to unify standards (colour gamut, bit depth, resolution, brightness range, etc.) and helps with selecting a new product.
An Ultra HD Premium sticker or label on the packaging, in the manual or on the device itself is a guarantee of full HDR support. So, if you have a Blu-ray player, a Blu-ray disc and an HDMI cable, you will see the images in the best possible quality.
UHDP Certification for Displays requires:
- Display Resolution of 3840×2160
- 10-bit colour depth
- WCG and BT.2020 input
- Reproduction of more than 90% P3
- HDR (SMPTE ST2084 EOTF)
- Brightness range of 0.05 - 1000 nits for LCD panels and 0.0005-540 nits for OLED panels
Also specified is the content that can be labelled with the Ultra HD Premium logo. It must meet the following requirements:
- Resolution of 3840×2160
- Colour depth of at least 10 bits
- BT.2020 colour range
- HDR (SMPTE ST2084 EOTF)
